Contents
Docker build
The docker build command can be used to create an image from an application.
$ docker build -t server_web_1 -f Dockerfile .
The -t flag represents the name and tag of the image (example: 'name:tag'), and -f is the name and path to the Dockerfile.
Docker run (Simple)
The docker run command is used to run a container from an image.
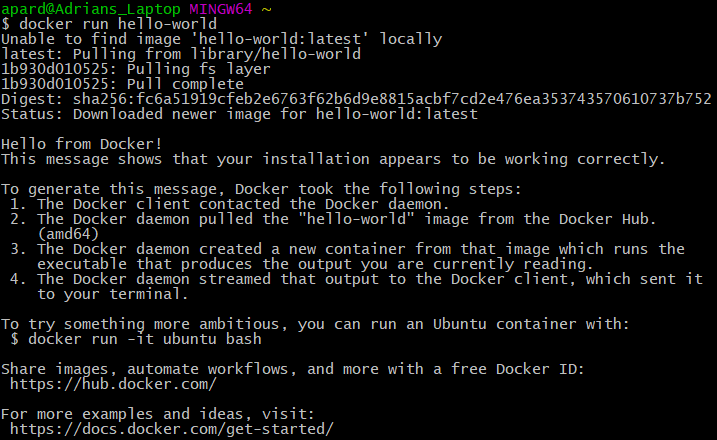
$ docker run hello-world
The "docker run hello-world" command will run an instance of the official hello-world image on the docker host if it already exists.
If the image is not present on the host, it will go out to docker hub and pull the image, but this is only done the first time. For the subsequent executions the same image on the host will be reused.
Docker run (Advance)
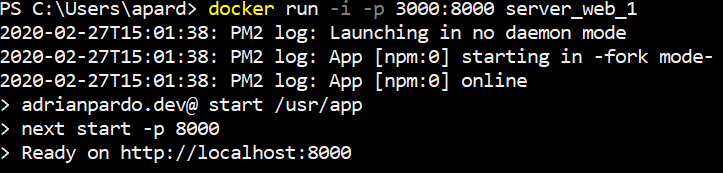
For this section, docker run will be executed on a web server.
$ docker run -i -p 3000:8000 server_web_1
The -i flag stands for 'interactive', meaning STDIN will stay opened.
The -p flag is for publishing a containers port. Here, this maps port 8000 in the Docker image to port 3000 on the local machine.
To run the docker image as a background task the -d (detach) flag can be used rather than -i. This will keep the terminal available:
$ docker run -d -p 3000:8000 server_web_1
Docker ps
The docker ps command lists all running containers.
$ docker ps
This command will also provide information about the running containers. Such as container ID, the image used to create the container, current status and a randomly generated name by Docker. In this example the name is "dreamy_hopper"
$ docker ps -a
Docker stop
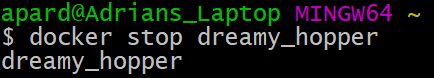
To stop a running container use the docker stop command. Either the container ID or name must be provided. We can use the "ps" command to get the container ID or name.
$ docker stop dreamy_hopper
Docker rm
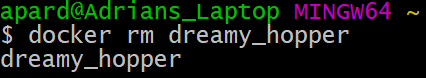
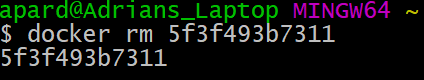
To permanently remove a stopped or exited container, the docker rm command can be used.
$ docker rm dreamy_hopper
If successful, the name or ID will be printed, like below:
To delete all containers, the following command can be used:
$ docker rm $(docker ps -a -q)
Docker images
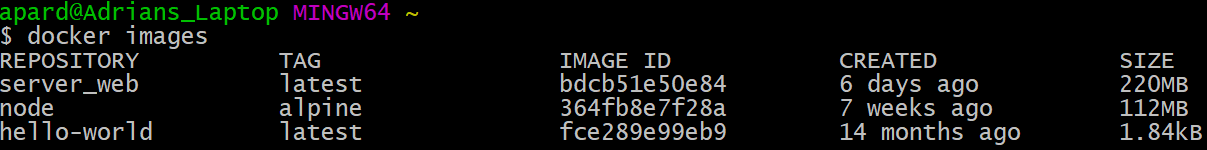
To see a list of images present on the host machine, the docker images command can be used.
$ docker images
Docker rmi
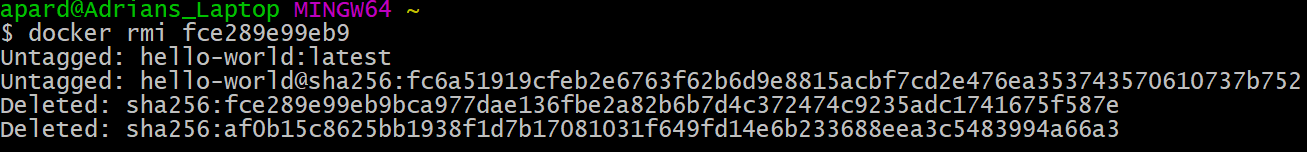
The docker rmi command can be used to remove an image that will no longer be used.
$ docker rmi
All dependent containers must be stopped and deleted, before being allowed to delete the image.
To delete all images, the following command can be used:
$ docker rmi $(docker ps -a -q)
Docker pull
Earlier when the command 'docker run hello-world' was executed, the image was downloaded and then ran.
To download an image but not run it, the docker pull command can be used.
$ docker pull hello-world
Docker exec
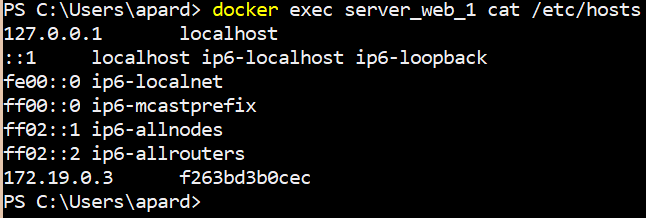
To run a command on a running container the docker exec command can be used.
$ docker exec server_web_1 cat /etc/hosts
This command will print the contents of the 'hosts' file, inside the running container 'server_web_1'.